In the digital pulse of today's high-tech era, batteries, fundamental to electronic equipment, have become the cornerstone of our daily lives and work. They are particularly crucial in small electronic devices, where the choice of the right battery can pivotally alter device performance. This article delves into the intricacies of LR44 vs 357 batteries—two coin cell variants ubiquitous in numerous small gadgets. Our exploration intertwines a detailed introduction with a juxtaposition of functions and performances, knitting together their limitations and advantages. This tapestry of information aims to arm readers with a comprehensive perspective, crucial for making informed decisions in varied application scenarios. We will pivot our focus to dissect the chemical composition, voltage characteristics, and capacity of these batteries. Simultaneously, we’ll touch on their applicable fields. Our goal? To crystallize a clear and authoritative guide on battery selection for our readers.
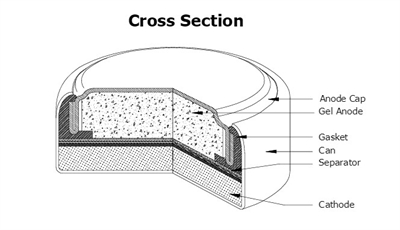
Figure 1: 357/303 Battery Cross Section
Catalog
The LR44 battery, an alkaline zinc-manganese button cell, is a familiar power source in portable electronics. Its accessibility and cost-effectiveness render it a favored choice for many small devices. With a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts, the LR44 boasts stable power delivery. Optimal performance is achieved at 20 degrees Celsius, although it functions effectively in temperatures ranging from 0 to 60 degrees Celsius.
Figure 2: LR44 Battery Characteristics
In devices like watches, computer motherboards, and medical equipment, the LR44 excels due to its size and balanced power output. The chemical makeup of this battery ensures stability during prolonged storage and usage. Yet, it's worth noting: while the LR44 shines in several areas, it may lag behind silver oxide batteries in energy density and voltage stability.
Shifting the focus to the 357 battery, we encounter a silver oxide-based contender, lauded for its extended lifespan and consistent voltage output. Sharing the 1.5 volts nominal voltage with the LR44, the 357 surpasses it in power conversion efficiency and longevity. This trait makes it ideal for devices needing steady, dependable power, including watches, medical apparatus, and laser pointers.
Figure 3: 357/303 Battery Temperature Characteristics
The Energizer 357, a standout in the market, has earned consumer trust through exceptional performance and high reliability. These mercury-free batteries align with contemporary environmental standards and boast an energy storage life of up to five years. This longevity minimizes frequent replacements, offering a robust power solution for devices demanding long-term, stable energy. The Energizer 357 strikes a harmonious balance between environmental stewardship and performance, marking it as an exemplary power source for today's electronic devices.
Figure 4: 357/303 Battery Storage Effects
The heart of modern electronic devices lies in the performance and specifications of their batteries. This makes the nuanced understanding of different battery types, such as LR44 and 357, essential for selecting the most suitable option.
Comparison of Specifications between LR44 Battery and 357 Battery
| model |
lR44
|
357
|
|
Battery type
|
Alkaline Manganese Batteries
|
Silver Oxide
|
|
Nominal Voltage
|
1.5V
|
1.55V
|
|
Nominal Capacity
|
120mAh
|
150 mAh
|
|
Operating Temperature Range
|
-10℃ to 60℃
|
|
|
Diameter(inch)
|
0.457inch
|
|
|
Diameter(mm)
|
11.6mm
|
11.6mm
|
|
Height(inch)
|
0.213inch
|
0.213inch
|
|
Height(mm)
|
5.4mm
|
5.4mm
|
|
IEC(JIS)
|
LR44
|
|
|
Mass(oz)
|
0.0705oz
|
|
|
Mass(g)
|
2g
|
2.3g
|
The LR44, a prevalent alkaline zinc-manganese battery, operates at a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts and a capacity of 120mAh. Its resilience is evident in its wide operating temperature range, from -10°C to 60°C. Dimensionally, it measures 11.6 mm in diameter and 5.4 mm in height, with a modest weight of about 2 grams. This compact form factor positions it as the preferred choice for small, portable devices. However, its voltage and capacity might limit performance in devices with more demanding power requirements.
Figure 5: LR44 Battery Specifications
Contrastingly, the 357 battery leverages silver oxide technology, offering a slightly higher nominal voltage of 1.55 volts and a capacity of 150mAh. This translates to a longer usage time and increased energy density compared to the LR44, a crucial factor for devices needing sustained usage or high energy efficiency. Size-wise, the 357 mirrors the LR44 in diameter and height but tips the scales slightly heavier at approximately 2.3 grams. While this minor weight disparity is negligible in most cases, it could be a consideration in the design and usage of certain precision instruments. This comparison not only highlights the technical differences but also underscores the importance of matching battery specifications to specific device requirements.
Figure 6: 357/303 Battery Specifications
Choosing the right battery type hinges on understanding the distinct capabilities and performance characteristics of each option. Despite their similar appearances, LR44 and 357 batteries diverge significantly in their performance and applications. This section aims to dissect these differences, guiding users towards more informed decisions for specific scenarios.
The LR44 battery's key strengths lie in its cost-effectiveness and consistent performance. This is attributed to the use of manganese dioxide as the cathode material. This not only curtails production costs but also guarantees steady battery operation. Particularly under high drain pulse discharge conditions, the LR44 provides stable voltage output—a critical aspect for devices needing quick response and stable power. Moreover, its anti-leakage capabilities are commendable. A unique sealing structure, coupled with special material treatment, bolsters the battery's safety and durability. In terms of environmental impact, the LR44 aligns with the European RoHS directive, steering clear of harmful substances like mercury, cadmium, or lead. This reflects a commitment to environmental protection inherent in modern battery technology.
Figure 7: LR44 Battery
The 357 battery, distinguished by its silver oxide chemistry, boasts a nominal voltage of 1.55 volts and a typical capacity of 195mAh. These specifications confer advantages in prolonged performance and energy density. Such traits make the 357 battery an optimal choice for devices like medical equipment and calculators, which demand a long-term stable power supply. The Energizer brand 357 batteries, mercury-free and capable of storing power for up to 5 years, underscore both environmental responsibility and long-term stability. Its versatility also merits attention; capable of replacing various button battery sizes, such as 280-03 battery, 357 303 battery, the 357 offers remarkable flexibility and convenience. This comparative analysis not only underscores the unique attributes of each battery type but also illuminates their suitability for different applications, aiding users in their selection process.
Figure 8: 357/303 Battery
While LR44 batteries have numerous strengths, they are not without their drawbacks. Primarily, these batteries are single-use, which leads to increased costs for users and environmental concerns. The high energy density of LR44 is a plus, but its overall capacity is modest, limiting its suitability for high-energy-demand devices. A notable point is its 1.5V voltage, potentially problematic in voltage-sensitive devices, particularly when juxtaposed with the 1.55V 357 battery. Furthermore, the cost of LR44 batteries, compared to other types like carbon-zinc or silver oxide batteries, can add a financial strain over long-term use.
The 357 battery, too, comes with its set of limitations. Echoing the LR44, it's also non-rechargeable, impacting its environmental and economic viability. A significant downside is its tendency for capacity loss during extended storage, a critical factor for devices used sporadically but requiring dependable long-term power. Temperature sensitivity is another limitation, particularly in high-temperature environments, which may impede its application in certain scenarios. Like the LR44, the cost of the 357 battery is relatively steep, especially when compared with alternatives like carbon-zinc or silver oxide batteries, a consideration for budget-conscious users. This comparison not only highlights the inherent constraints of these batteries but also aids users in weighing their options based on specific needs and usage conditions.
Figure 9: 357/303 Battery
Size profiles play a crucial role when choosing between LR44 and 357 batteries. While these batteries share similarities, subtle size differences are pivotal in determining their compatibility and performance in specific devices.
The LR44, a cylindrical battery, adheres to standard dimensions: 11.6 mm in diameter and 5.4 mm in height. This compact size renders the LR44 ideal for various small electronic devices, notably in slim designs such as watches, miniature remote controls, and select medical devices. For users opting for an LR44 battery, ensuring a precise fit is imperative to avert performance issues or potential damage from an ill-suited size.
Figure 10: LR44 Battery Dimension
The 357 battery mirrors the LR44 in shape and size, with identical dimensions of 11.6 mm in diameter and 5.4 mm in height. This uniformity in size means that devices designed for LR44 batteries can often accommodate 357 batteries, offering a level of interchangeability. However, users should not overlook other crucial factors when choosing a 357 battery. It's essential to consider the battery's chemical makeup and voltage characteristics to guarantee not only a snug fit but also compatibility with the device's performance requirements. This nuanced comparison highlights the importance of considering both physical and technical aspects when selecting a battery, ensuring optimal functionality and device integrity.
Figure 11: 357/303 Battery Typical Discharge Characteristics
In the realm of small electronic devices, LR44 batteries are indispensable due to their compact size and efficient energy output. Ubiquitous in everyday life, they power a diverse array of gadgets, including calculators, watches, and digital thermometers, meeting their basic power requirements with stable performance. Beyond these common uses, LR44 batteries are integral to medical devices, children's toys, and electronic games, offering the sustained and reliable power vital for their proper functioning. The reliability and high energy density of LR44 batteries underscore their suitability as a preferred power source in these applications.
In contrast, 357 batteries cater to devices with more intensive power demands. They are particularly crucial in medical equipment, delivering the essential, long-term stable power supply. Beyond medical applications, 357 batteries are also employed in smaller electronic products like watches, calculators, and cameras, where higher performance standards are essential, especially regarding battery life and voltage stability. Owing to its extended service life and more consistent voltage output, the 357 battery emerges as the go-to choice in these areas. In specific applications, the high performance of 357 batteries guarantees the reliable functioning and long-term stability of devices, a critical factor in demanding scenarios such as precision instrumentation and professional photography equipment. This delineation not only illustrates the distinct roles of LR44 and 357 batteries but also emphasizes their tailored suitability for various technological needs.
For devices with high energy demands, the 357 battery often emerges as the superior choice. Its higher nominal capacity and sustained power output make it ideal for equipment like specialized medical instruments and advanced photography gear, which require unwavering battery stability and continuous output. Opting for 357 batteries not only guarantees stable equipment operation but also prolongs service life and minimizes maintenance needs. In contrast, LR44 batteries are more apt for medium energy consumption devices, like everyday digital gadgets and children's toys, balancing sufficient power delivery with cost-effectiveness.
Figure 12: 357/303 Battery
In the precision instrument domain, particularly for watches and medical devices, the 357 battery is preferred due to its prolonged service life and stable voltage output. These devices necessitate enduring reliability and battery performance, a criterion met by the 357's high-performance attributes. Meanwhile, LR44 batteries are a fitting choice for equipment with less stringent accuracy demands, adequately powering basic operational needs.
Considering the frequency of battery replacement and long-term costs, 357 batteries stand out. Their extended service life reduces the need for frequent replacements, offering convenience and potential long-term economic benefits. Conversely, LR44 batteries might require more frequent replacements in high-energy devices, potentially leading to increased long-term expenses.
Regarding shelf life, 357 batteries typically boast up to 5 years, underscoring their longevity and stability. LR44 batteries, on average, have a shelf life of around 3 years, although newer models can extend this to 4-5 years. Nonetheless, the 357 battery generally holds the advantage in this aspect.
From a cost-effectiveness standpoint, while LR44 and 357 batteries deliver commendable performance in certain scenarios, they may not always represent the most economical choice, particularly when compared to carbon-zinc or some silver oxide batteries. Users seeking a balance between performance and cost might find these alternatives more budget-friendly in specific applications. This comprehensive analysis helps users navigate the complexities of choosing between LR44 and 357 batteries, factoring in various aspects from energy demands to economic considerations.
LR44 batteries, frequently utilized in low-power devices such as calculators, small remote controls, and watches, demonstrate varied service life based on device type. In low-consumption settings, an LR44 can function for up to two years, a testament to its stable discharge characteristics and moderate current output. With an average capacity ranging between 110-130mAh, these batteries adeptly adapt to diverse scenarios.
In contrast, when employed in moderately demanding devices like children's toys or digital thermometers, the LR44's discharge performance is influenced by several factors. These include the rate of discharge, usage patterns (continuous versus intermittent use), and the device's energy requirements. While the LR44 remains an option in these cases, these variables may curtail its lifespan.
Figure 13: LR44 Battery
The 357 303 battery, with its unique silver oxide chemistry, typically outlasts the LR44. Its chemistry boosts energy density, offering capacities often in the 150-200mAh range, or higher. This makes the 357 a more suitable candidate for high-energy applications, particularly in precision devices demanding long-term, stable power.
For equipment with rigorous power stability and durability needs, such as medical monitors and professional cameras, the battery 357 presents considerable benefits. Its lifespan often exceeds that of LR44 batteries by 30% to 100%, a significant factor for devices requiring prolonged, uninterrupted operation.
In choosing between LR44 and 357 batteries, consider your device's specific needs, anticipated usage patterns, and battery life expectations. While LR44 may offer initial cost savings, 357 batteries excel in long-term stability and efficiency. Thus, for high-precision devices needing consistent, long-term power, opting for 357 batteries is a judicious choice. This analysis underscores the importance of aligning battery selection with device requirements, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
LR44 and 357 batteries, while similar in appearance, diverge significantly in performance and application. This section delves deeper into their characteristics, highlighting key differences.
LR44, an alkaline battery type, typically operates at a nominal voltage of 1.5 volts. Its voltage output gradually declines during discharge, reaching a cut-off point of around 0.9-1.0 volts. This characteristic implies potential issues for voltage-sensitive devices, such as certain watch models, as they near depletion. Advancements in battery technology have pushed the shelf life of high-quality LR44 batteries to 4-5 years, offering users extended usage and improved economic benefits. In terms of cost, LR44 batteries enjoy widespread market popularity, largely due to their affordability, especially at hardware stores and online platforms.
Figure 14: LR44 Battery Discharge curve
On the other hand, the silver oxide 357/303 battery boasts a higher nominal voltage, around 1.55 volts, enhancing its power supply stability. The 357 experiences a lesser voltage drop during usage, making it ideal for devices that require a constant, stable voltage. These include high-precision watches, advanced calculators, and certain vital medical equipment. Typically, 357 batteries have a nominal capacity between 150-200mAh, and in low-consumption scenarios, this can exceed 200mAh. A key advantage of the 357 is its remarkably low self-discharge rate, coupled with a shelf life of up to 5 years. This is particularly beneficial for devices needing long-term storage or infrequent battery changes. Moreover, as a zero-mercury product, the 357 battery's environmental footprint is minimal, aligning with growing ecological concerns.
In choosing between LR44 and 357 batteries, users must weigh factors like voltage stability, capacity, shelf life, and environmental impact. LR44 batteries are more suited to budget-conscious and less frequently used devices. Conversely, 357 batteries are preferable for applications demanding higher voltage stability and eco-friendliness. Understanding the distinct attributes of both battery types enables users to make informed decisions, ensuring their devices operate optimally and last longer.
LR44 Battery: LR44 is a 1.5V battery and its rated voltage is 1.5V. The LR44 is well-suited for standard electronic products like remote controls and small flashlights, which don’t demand stringent voltage precision.
Figure 15: LR44 Battery
357/303 Battery: Boasting a slightly higher rated voltage of 1.55V, the 357 excels in devices requiring more precise voltage, such as high-end watches and medical equipment.
LR44 Battery: Voltage stability declines with use, fitting for devices where high voltage stability isn't paramount. However, voltage-sensitive devices might find this a drawback.
357/303 Battery: The silver oxide chemistry of the 357 ensures more stable voltage output throughout its life cycle, crucial for precision instruments with stringent voltage requirements.
LR44 Battery: Voltage decrease can impair performance in voltage-sensitive devices like electronic clocks and certain sensors.
357/303 Battery: Stable voltage output enhances device reliability and performance, particularly in high-accuracy applications.
LR44 Battery: Despite high energy density, it may falter in high-energy-demand applications.
357/303 Battery: Its superior energy density, a result of its higher rated voltage, is ideal for energy-intensive devices like high-performance medical tools and professional audio equipment.
Figure 16: 357/303 Battery
LR44 Batteries: Voltage diminishes to 1.0V or lower over time, potentially impacting device performance.
357/303 Battery: Maintains a comparatively consistent voltage output until end-of-life, dropping to about 1.2V, favoring precision equipment with high voltage stability needs.
Precision Instruments: LR44 suits equipment that can tolerate voltage drops, whereas 357 is optimal for precision devices demanding consistent voltage stability, like high-end medical monitors.
Equipment Reliability: LR44’s reliability may wane when voltage drops below 1.0V. Conversely, 357 offers more stable performance and heightened reliability.
LR44 Battery: Voltage drop to 1.0V or lower typically signals the need for replacement.
357/303 Battery: Exhibits more stable voltage until its end-of-life, providing more predictable performance down to 1.2V.
Overall, when selecting between LR44 and 357 batteries, it’s crucial to weigh their respective voltage characteristics, stability, energy density, and the specific requirements of your application scenario. A thorough understanding of these factors is key to ensuring the chosen battery aligns with your device's performance and reliability expectations.
In the intricate world of battery replacements, discerning the equivalents and compatibilities of LR44 batteries is essential. The LR44, a prevalent alkaline coin cell, boasts a variety of equivalent models in the market, each sharing certain key characteristics.
LR44 Battery Equivalent Models: A76, AG13, L1154, LR1154, 157. These models are not only dimensionally identical to the LR44 but also mirror its alkaline makeup and 1.5V voltage. This congruence enables their interchangeable use.
However, a distinction arises with certain batteries like SR44, SR44SW, 303, and 357. These silver oxide coin cells, while akin in size to the LR44, diverge in chemistry and voltage. Offering a slightly elevated voltage of 1.55V, they also tend to have a longer lifespan.
Choosing a Replacement: Essential Points
Compatibility Check: Dimensional similarity isn’t the sole criterion. For device safety and optimal performance, a battery compatible with the original specifications is vital. Mismatched chemistry or voltage might lead to over- or under-discharge, jeopardizing the device’s functionality or integrity.
Device Requirements: Always refer to the device’s manual before replacing a battery. It’s crucial to understand the specific requirements, including voltage, capacity, and chemical composition.
Environmental Impact: The environmental aspect is increasingly significant. Silver oxide batteries, for instance, may offer a greener option. Therefore, environmental considerations should also guide your choice.
By meticulously selecting the appropriate battery, users not only safeguard their devices’ performance but also contribute to prolonging their lifespan and minimizing environmental impact. Thus, when replacing an LR44 battery, factors like size, voltage, and chemical composition must be meticulously weighed.
Renowned for its versatility, the 357 battery, a button battery, finds extensive use in a plethora of small electronic devices. Its uniform size and voltage traits have spawned numerous equivalent alternatives in the market. These equivalents are a boon to both consumers and technicians, offering a breadth of choice and convenience. In the realm of electronic components, the significance of such equivalent parts cannot be overstated; they guarantee not just equipment flexibility but also repair viability. This segment delves into several key equivalents of the 357 battery, such as the SR44, AG13, A76, SG13, and PX76A. Not merely replicas in size and voltage, these counterparts are akin in performance and application scopes, rendering them optimal substitutes in certain scenarios.
The SR44, a prevalent equivalent to the 357, matches it in every dimension: 11.6 mm in diameter and 5.4 mm in height, with a voltage of 1.55 volts. This makes the SR44 an impeccable stand-in. But there's more: its chemical composition echoes that of the 357, predominantly utilizing silver oxide. This choice of material ensures longevity and stable voltage output, catapulting the SR44 to popularity, especially in devices demanding sustained power, like precision instruments and medical gear. From an expert's perspective on electronic components, the SR44's high compatibility and dependability in replacing 357 batteries are noteworthy.
Matching the 357 in size and voltage, the AG13 emerges as another viable alternative. Its universal acceptance stems from its broad compatibility and ready availability. Like the SR44, this 1.55-volt silver oxide battery is known for stable voltage and extended shelf life. The AG13's prevalence in everyday devices - from toys to calculators - is undeniable. Its widespread availability across retailers and online platforms is a major plus for consumers needing swift replacements. In the lens of an electronics specialist, AG13 epitomizes the trend towards standardization in battery tech, maintaining uniformity in performance and dimensions across various brands.
The A76, sharing the 357's voltage (1.55 volts) and 11.6 mm diameter, stands out as another equivalent. Its universal appeal as a standard battery, used in devices ranging from remote controls to small lamps, is evident. A key aspect of the A76 is its affordability, an important factor for budget-conscious consumers. From a professional viewpoint in electronics, the A76 exemplifies how market needs can be met through standardization and cost-efficiency while preserving quality and reliability.
SG13 and PX76A, both mirroring the 357 in size and voltage, are crucial in their respective niches. The SG13, compatible with a variety of devices, is often chosen for special uses like high-precision instruments and certain medical tools, necessitating exceptional battery reliability and stability.
The PX76A, prevalent in photography and imaging equipment, shares the 357's dimensions but is preferred in some cameras due to its unique chemistry and durable performance. This battery's ability to provide consistent long-term power is a key benefit for prolonged use in photographic equipment.
Despite the differences in chemical composition and power generation between LR44 and 357 batteries, they can be interchangeably used in certain circumstances. However, understanding the implications and key considerations of swapping these batteries is crucial.
357 Battery: Exhibiting a nearly constant voltage output until chemical energy depletion, the silver oxide 357 is optimal for precision instruments needing consistent voltage, like high-end watches and precise measuring tools.
LR44 Batteries: Conversely, LR44 alkaline batteries experience a gradual voltage decline over time, making them less suitable for voltage-sensitive devices.
Advantages of 357 Batteries: With their generally larger capacity, 357 batteries cater well to devices demanding more energy, including specific medical and professional photography equipment, providing stable, efficient power over extended periods.
Limitations of LR44 Batteries: The LR44's lower mAh capacity and voltage might lead to subpar performance or decreased service life when used in devices designed for 357 batteries.
Physical size similarity allows LR44 and 357 batteries to fit the same battery slots, but several factors must be considered:
Device’s Voltage and Capacity Needs: Assess if the device can handle a gradual voltage drop and its specific capacity requirements.
Long-term Use and Stability: For devices needing prolonged usage and high voltage stability, 357 batteries typically emerge as the better option.
Economics and Availability: Factor in the cost-effectiveness and local market availability of these batteries.
In summary, while LR44 and 357 batteries can sometimes be used interchangeably, selecting the appropriate battery hinges on understanding their performance differences and the specific needs of the equipment. The right choice not only guarantees optimal device performance but also contributes to extending its lifespan and enhancing the user experience. Thus, although interchangeable in certain situations, the ideal battery choice is contingent on the particular requirements of your device and usage context.
In the diverse world of battery technology, alkaline and silver oxide batteries offer distinct performance characteristics due to their unique chemical compositions. This section dives into an in-depth analysis of their chemical makeup, voltage characteristics, capacity, and suitable applications, aiding users in discerning the best fit for their specific needs.
The Similarities and Differences between Alkaline Batteries and Silver-Oxide Battery
|
Chemistry
|
Alkaline
|
Silver-Oxide
|
|
Nominal Voltage
|
1.5V
|
1.55V
|
|
End-Point Voltage
|
1.0V
|
1.2V
|
|
Notes
|
Voltage drops over time
|
Very constant voltage
|
|
Typical Labels
|
LR44,76A,AG13,LR1154,A76
|
SR44W,SR44,SR44SW,157,357,
303,SG13,AG13,S76,A76,SR1154
|
|
Typical Capacity
|
110-130 mAh
|
150-200 mAh
|
Alkaline batteries, encompassing models like LR44, 76A, AG13, and LR1154, typically operate at a nominal 1.5 volts, descending to a cut-off voltage of around 1.0 volts. A notable trait is the gradual voltage decline with usage, with capacity generally ranging from 110-130mAh. While cost-effective, these batteries pose a leakage risk during prolonged storage or use, potentially corroding and damaging devices such as watches or small electronics.
Silver oxide variants, including SR44W, SR44, 157, and 357 models, maintain a nominal voltage of 1.55 volts and a cut-off voltage near 1.2 volts. Their standout feature is the remarkably stable voltage output, remaining consistent throughout their lifespan. With capacities usually between 150-200mAh, they offer 50% to 100% more longevity than alkaline batteries, doubling their service life. High energy density and strong current output make them ideal for devices demanding stable power, such as precision calculators and advanced medical and photographic equipment. However, these batteries are unsuitable for recharging, owing to their chemical composition.
When weighing alkaline against silver oxide batteries, consider the specific demands of your equipment and its operating environment. Alkaline batteries suit every day, low-power devices due to their affordability and availability. In contrast, silver oxide batteries excel in high-precision, high-stability environments, offering enhanced service life. Understanding these variances is key to ensuring your battery selection optimally aligns with your device’s performance and longevity needs.
LR44 and 357 batteries, critical in powering small electronic devices, share similarities in size and shape but diverge markedly in chemical composition, voltage stability, capacity, and their respective application domains. The LR44, lauded for its cost-effectiveness and broad availability, often becomes the default choice for numerous devices. In contrast, the 357 batteries, with their extended service life and superior voltage output, are particularly favored in precision equipment.
The decision to choose the right battery transcends basic device performance, delving into the realms of cost-efficiency and environmental impact. This article's thorough exploration aims to offer a valuable resource for users in making informed battery selections, ensuring that their devices function optimally and dependably across varied environments. As we embrace technological advancements, equal importance must be placed on evolving battery technologies, steering toward a future of sustainable and eco-friendly electronic device usage.
|
Characteristic
|
LR44
(Alkaline)
|
357
(Silver Oxide)
|
|
Chemistry
|
Alkaline
|
Silver
Oxide
|
|
Voltage
|
1.5V
|
1.55V
|
|
Capacity
|
Generally
lower capacity
|
Higher
capacity (often 30% to 100% longer lifespan)
|
|
Size
|
5.4mm
diameter, 11.6mm height (taller)
|
5.4mm
diameter, 9.5mm to 9.6mm height (shorter)
|
|
Voltage
Stability
|
Voltage
drops steadily as it discharges
|
Relatively
constant voltage output
|
|
Rechargeable
|
Typically
non-rechargeable
|
Typically
non-rechargeable
|
|
Lifespan
|
Average
lifespan with moderate energy demands
|
Longer
lifespan, suitable for higher energy demands
|
|
Cost
|
Generally
less expensive than 357
|
Generally
more expensive than LR44
|
|
Common
Applications
|
Various
electronic gadgets, watches, calculators
|
Watches,
calculators, toys, medical devices
|
Frequently Asked Questions [FAQ]
1. What Uses 357 Battery?
The 357 battery, a staple in the realm of precision equipment, thrives in the compact yet demanding environments of watches, electronic calculators, laser pointers, lighting, and medical devices like digital thermometers, even extending its utility to certain digital cameras. This silver oxide battery, celebrated for its diminutive stature, boasts a stable voltage, making it the go-to choice for small electronic devices that demand exceptional battery performance.
2. Is LR44 the Same As 357 303?
Intriguingly, although the LR44 and the 357/303 batteries share a resemblance in size, they diverge fundamentally in their chemical makeup and voltage outputs. The LR44, an alkaline variant, outputs a standard voltage of 1.5 volts. Contrast this with the 357/303, a silver oxide contender, slightly edging out with 1.55 volts. Despite their similar dimensions, this seemingly negligible voltage discrepancy holds the potential to significantly sway performance in devices of a more sensitive nature.
3. Is 357 Battery the Same As LR41?
When it comes to the 357 and LR41 batteries, differences are pronounced in their chemical composition, size, and voltage. The LR41, smaller and alkaline, operates typically at 1.5 volts. Meanwhile, the 357, a 1.55-volt silver oxide battery, stands distinct. Their differences render them non-interchangeable in the majority of devices.
4. What Is the LR44 Battery Used for?
The LR44, a ubiquitous presence in the world of small round alkaline batteries, finds its place in toys, watches, calculators, hearing aids, and a selection of small medical equipment.
5. Can I Replace LR44 with LR41?
While the LR44 and LR41 may mirror each other in voltage, both offering 1.5 volts, their size sets them apart. The LR41's smaller form factor means it cannot directly substitute for the LR44 in most devices, barring instances where device design accommodates such size variability. Though theoretically possible, should the battery slot's dimensions align and voltage requirements match, consulting the equipment manual or seeking expert advice remains a prudent step.
















 ABOUT US
Customer satisfaction every time. Mutual trust and common interests.
ABOUT US
Customer satisfaction every time. Mutual trust and common interests.
 LM358 Dual Operational Amplifier Comprehensive Guide: Pinouts, Circuit Diagrams, Equivalents, Useful Examples
LM358 Dual Operational Amplifier Comprehensive Guide: Pinouts, Circuit Diagrams, Equivalents, Useful Examples
 7408 Logic Gate Chip Ultimate Guide: Pinout, Characteristics and Applications
7408 Logic Gate Chip Ultimate Guide: Pinout, Characteristics and Applications
 CGA4F4NP02W222J085AA
CGA4F4NP02W222J085AA 2220PC105KAT1A
2220PC105KAT1A 06031A120MAT4A
06031A120MAT4A 06031U470GAT9A
06031U470GAT9A HMJ316BB7473MLHT
HMJ316BB7473MLHT 18125A821KAT2A
18125A821KAT2A T491A685K016AT
T491A685K016AT T491D336K035AT
T491D336K035AT CWR11KH475KD
CWR11KH475KD SM02B-SURS-TF
SM02B-SURS-TF